By now most marketers understand that graphic design has value in content marketing. LinkedIn posts with an image get twice as much engagement. Marketers using visual content marketing experience 27% higher click-through rates. A picture is worth a thousand words.
But, one area where graphic design gets slept on is search engine optimization. Most companies focus solely on written content when considering SEO. In fact, images can play a big part in how your site is ranked, how you appear in SERPs, and your overall SEO success.
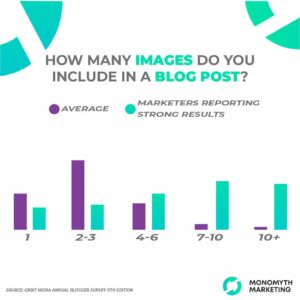
While most blogs include images, bloggers achieving strong results average 7 or more images per post. Why do they see higher success? What role does graphic design play in SEO?
Enhance User Experience through Graphic Design
The main driver for any content marketing decisions should be whether it improves the user experience. One measure of this is time on page. How long are your blog posts and other content being consumed?
Websites with an above-average time on site tend to rank higher on Google. In fact, the average time on site for a Google first page result is 2.5 minutes.
Here are a few ways you can use images and graphics to improve time on site and user experience:
Use Images to Enhance Readability
Your blog will receive two types of visitors. A very small percentage of visitors will read your entire blog post from start to finish. The larger percentage are skimmers who will scan over the content and only read what grabs their attention.
You can optimize for skimmers with headers, bullet points, bold and italic text, quotes and…images! Images are a great way to break up large blocks of text and engage readers who otherwise wouldn’t continue with your content.
Images are also a much more engaging and effective way to convey your message.
Use Visual Hierarchy to Guide User Interaction
In addition to time on page, Google tracks the dwell time of how long visitors spend looking at your entire website. Your goal as a marketer should be to guide visitors through your website from top-of-funnel blog content to mid-funnel content such as further blog posts and case studies, to conversion pages. Graphic design can be used to create a visual hierarchy that guides users through this flow.
Design elements like contrasting colors, bold fonts, and well-placed calls-to-action (CTAs) can direct users through your site, encouraging conversions and longer sessions.
Incorporate Infographics and Shareable Visual
While stock images, memes, embedded videos, CTAs, and third-party graphics can all increase readability and guide user flow, creating your own original content will bring the most benefit.
Original graphics with useful information can attract backlinks, a key SEO ranking factor. Shareable content also increases your chances of social shares, which can indirectly affect SEO.
Optimize Images for SEO Performance and Speed
Simply including high-quality, valuable images in your content can help boost SEO. However, the real boost comes from optimizing those images to ensure they load correctly and provide additional data to search engines.
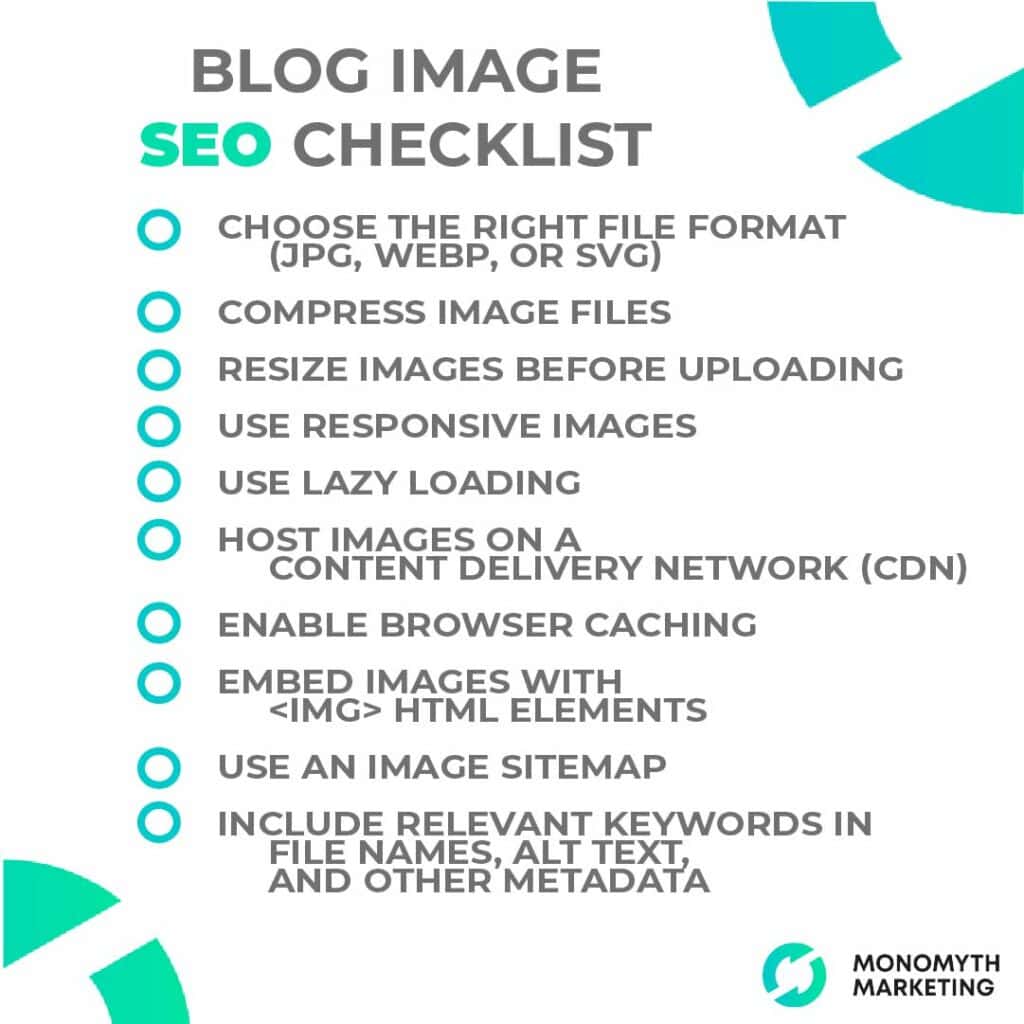
Optimize Image Sizes and Formats
Filling your pages with a lot of large image files, plugins, and other rich media can drastically slow down your page load time. Aim for a page load score under 3 seconds to avoid losing visitors and search ranking. Here are a few steps to take:
- Choose the right file format. In general, JPEGs are smaller files compared to PNGs. However, WebP is a new image format that provides lossy and lossless compression for images on the web. According to Google, WebP lossless images are 26% smaller in size compared to PNGs and 25-34% smaller than comparable JPEG images. Unless you need very high-resolution images, opt for WebP. For icons and logos, use SVG as the scalable vector graphic can be scaled down to any size without losing resolution and without resulting in a large file size.
- Compress image files. I mentioned lossy and lossless a second ago. Lossless compression means the image still keeps all its data. Lossy compression removes some data (and image quality) to reduce the file size even further. Use compression tools like TinyPNG, JPEG-Optimizer, or WordPress plugins like Smush and Imagify to automatically compress your site images.
- Resize images before uploading them. If your site design and web browsers are already going to resize images on your site, there’s no reason to upload a 3000 x 5500 pixel image. Consider your website’s max site width and upload images that fit.
- Use responsive images. Along the same lines, there’s no reason to display a large image if your visitor is viewing your website on a 2-inch cellphone screen. Use responsive images to make sure browsers load images sized for the visitor’s device.
- Use lazy loading. If you’re following best practices and including 10+ images with every blog post, that is still a lot of images to load all at once. Instead, use lazy loading so images are only loaded when the visitor scrolls down to them. This speeds up the site’s initial load time to avoid visitors immediately bouncing off your page.
- Serve images from a content delivery network (CDN). A CDN like Cloudflare or StackPath can serve your images from a server closer to the visitor’s location, automatically reduce file sizes, and improve load times.
- Enable browser caching. Browser caching means returning visitors don’t have to re-download the same images. This improves the user experience for returning visitors and for users visiting multiple pages on your website.
Google Image SEO Best Practices
Google provides a guide for image SEO best practices to optimize how Google discovers your images and displays them in search results.
- Use HTML elements to embed images. Google doesn’t index CSS images. Make sure the images are contained within a <img> element.
- Use an image sitemap. Submitting an image sitemap helps Google discover images it may have otherwise missed. This is especially important if you’re using a CDN.
- Responsive images. If you’re using responsive images, make sure to use the <srcset> attribute so Google can find the source image.
- Use supported image file formats. Google Search supports BMP, GIF, JPEG, PNG, WebP, SVG, and AVIF.
- Optimize image landing pages and metadata. The actual page where the image is embedded should be optimized for SEO with a relevant page title, description, structured data, filenames, and alt text. Google warns against keyword stuffing in alt text and instead recommends a good, long-tail keyword that accurately describes the image.
 Improve Content Shareability and Discoverability
Improve Content Shareability and Discoverability
Blog posts that are shared and hyperlinked enjoy much higher rankings on Google and other search engines. They also serve to expand your audience and increase page views.
Images are one of the best ways to increase your blog’s shareability and discoverability. Buzzsumo found that articles with one image every 75-100 words were shared twice as often as articles with fewer images.
Images are much easier to share and have the potential to more clearly and succinctly convey the messages of your content. Most social network algorithms like Facebook and LinkedIn also weigh visual content much more heavily compared to text and links.
Here’s how to improve your image content’s shareability and discoverability:
- Optimize Link Preview Images: Control which featured image will appear when your article is shown on search results pages and social networks. There’s nothing worse than LinkedIn automatically creating a nice big link preview image and it’s just some random site icon. Make sure your featured images will look great as preview images and help promote the content.
- Size Images for Social Media: If your blog post includes potentially shareable images like graphs and diagrams, make sure their dimensions will look good when shared on social. In general, a 1:1 aspect ratio will show up well on most sites. You may also want to use a higher-quality image around 1080 x 1080 pixels. Weigh this benefit against the page load times mentioned above.
- Google Image Search: Optimizing your metadata, alt text, and captions will help your images appear in Google Image search results. If your audience is looking for a chart or diagram to break down their problem or query, this is likely a much less crowded space compared to the main search page.
- Use Original Images: Stock images are cheap and easy to use, which is why they are the most common image type for marketers. They also see the worst results. Creating great, original image content makes it much more likely to be shared. It will also show up higher on Google Image searches.
 Measure the Impact of Graphic Design on SEO
Measure the Impact of Graphic Design on SEO
Once you start using graphic design to improve your user experience, increase content shareability, and optimize image performance, you need to measure the impact of these efforts on SEO. There are several tools you can use to analyze website performance, SEO, and content marketing efforts.
Here are some tools I recommend using and metrics to focus on:
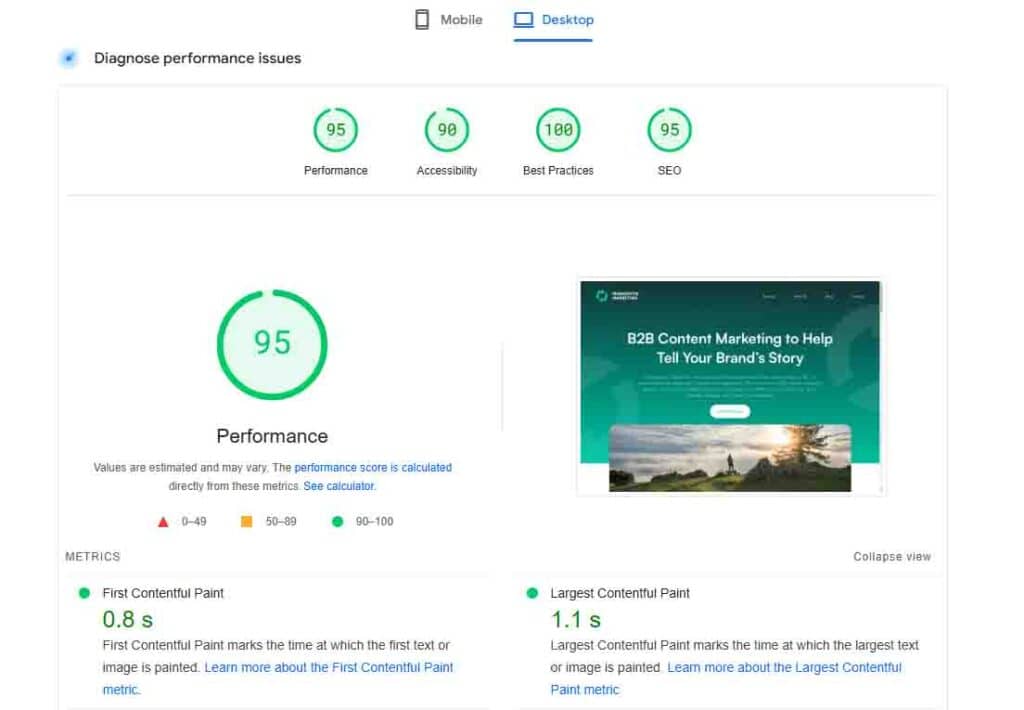
Google PageSpeed Insights
PageSpeed Insights measures the user experience of a page based on real-user experience data and performance, accessibility, and SEO audits run through Lighthouse. PageSpeed Insights provides scores on performance, accessibility, best practices, and SEO and offers specific diagnostics to help target improvements.
For a more advanced view, consider investing in a website performance monitoring tool like GTmetrix or Pingdom to identify specific images that are slowing your website performance and hurting SEO.
 Google Analytics and Search Console
Google Analytics and Search Console
You’re probably already using these tools to measure your content ranking, traffic, and conversions. You can also use these tools to measure the ranking and performance of specific images and other multimedia content. Make sure your images have the proper tracking elements in the data layer and set up specific reports to see organic traffic coming from Google Image Searches and to learn how often your images are shared.
SEMrush Site Audit
SEMrush’s Site Audit tool is valuable for finding website elements affecting load times or not following SEO best practices. In the Issues tab of the Site Audit, you can search for images that need improvement, including:
- Images that aren’t working (usually because the file was deleted)
- Images slowing page load speed
- Images missing alt attributes
- Images that aren’t accessible to search engines
A/B Test
Using A/B testing to see how your new graphic design strategy impacts SEO. Use A/B testing tools like HubSpot or Optimizely to test different image styles and placements to find what works best for your audience.
High-quality graphics may increase your content budget. A/B testing pages with images and pages without can be a good way to justify your investment in graphic design.
Heatmaps
Getting a better understanding of how users are interacting with your website and content can help you better tailor your images and user experience. Heatmap software such as Mouseflow or Hotjar shows you which parts of your website attract the most attention and where you might have problems with customer experience.
As I mentioned, graphic design can create a visual hierarchy to guide user interaction. Heatmapping can help you identify where your users are currently being drawn and help you measure efforts to optimize website visits.
Have you been neglecting graphic design as part of your SEO strategy? It’s time to do more than attach a featured image to your blog posts and call them optimized.
If you need help navigating the technical and design aspects of using images to improve SEO, Monomyth Marketing can help! Our designers and SEO experts can build great visuals that improve shareability and help boost your search rankings. Learn more about our graphic design services.